multicycle datapath 실행과정
1) instruction fetch
2) instruction을 해독하고 register을 fetch 한다.
3) 실행, 메모리주소 계산, branch 하기 (branch instruction 끝)
4) 메모리 access 혹은( r-type instruction 완료)
5) 업데이트 (lw 완료)
1. Instruction fetch
IR <- Memory [PC]
PC ← PC + 4

2.Instruction decode and register fetch
A ← Reg[IR[25-21]] (RS)
B ← Reg[IR[20-16]] (RT)
ALUOut ← PC + (sign-extension(IR[15-0]) << 2 (Branch를 위한 target address)

-> 2단계 까지는 어떤 명령어든지 공통적으로 모두 일어남
3.Instruction dependent
명령어의 종류에 따라 다른 과정이 일어남
lw, sw : memory reference (메모리 접근)
ALUOut ← A + sign-extension(imm16)
instruction reg > sign-extension(imm16) > ALUOut <- A + sign-extension(imm16)

R-type : add, or, and , sub , slt
ALUOut ← A op B

Branch : beq , bne
if(A==B) PC ← ALUOut
ALU 에서 A와 B의 값을 비교 > mux에서 pc+4를 보낼지 ALUOut 값을 보낼지 결정 (branch는 여기서 끝)

4. R-type or memory access
- lw, sw 를 위해 memory access를 한다. or R-type instruction을 완료한다.
Load(I-format)
MDR <- Memory[ALUOut]
ALUOut의 값을 memory access 레지스터에 넣고 해당 주소의 값으로 MDR 업데이트
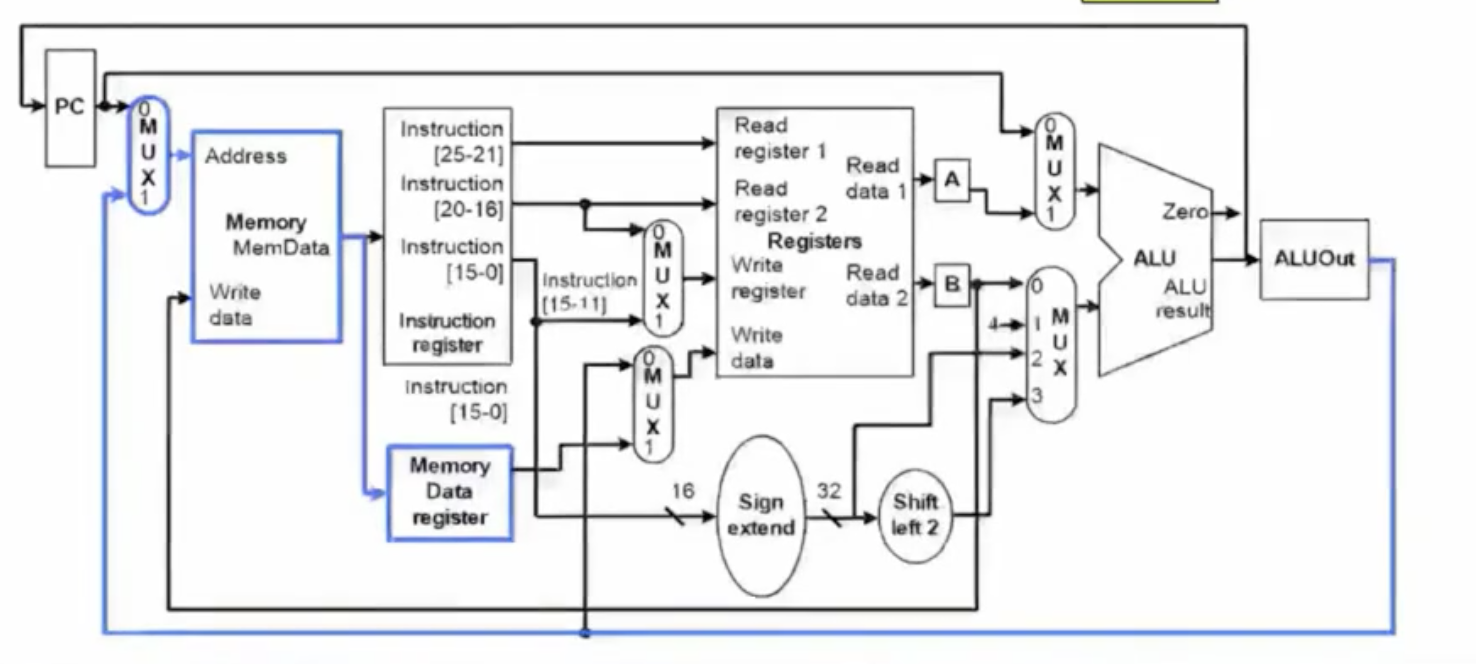
Store(I-format)
memory[ALUOut] <- MDR
- 세번 째 clock cycle에서도 같은 값이 입력되기 때문에 상관없음
ALUOut 값과 rt 값이 보내진다. > ALUOut 에 해당하는 메모리에 rt 값을 저장

R-format (R-format 끝)
Reg[IR[15-11]] (Rd) <- ALUOut

5. Memory read completion step (Lw 만)
'ੈ✩‧₊˚Computer Science > 컴퓨터구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [컴퓨터구조]Data hazard (forwarding) (0) | 2020.11.17 |
|---|---|
| [컴퓨터구조] Pipelining Hazard (파이프라인 해저드) (0) | 2020.11.13 |
| [컴퓨터구조] single cycle 의 단점, multi cycle (0) | 2020.11.06 |
| [컴퓨터구조] Datapath 간단한 설계 (0) | 2020.10.30 |
| [컴퓨터구조] 데이터패스(Datapath) 명령어 실행(MIPS) (0) | 2020.10.30 |


